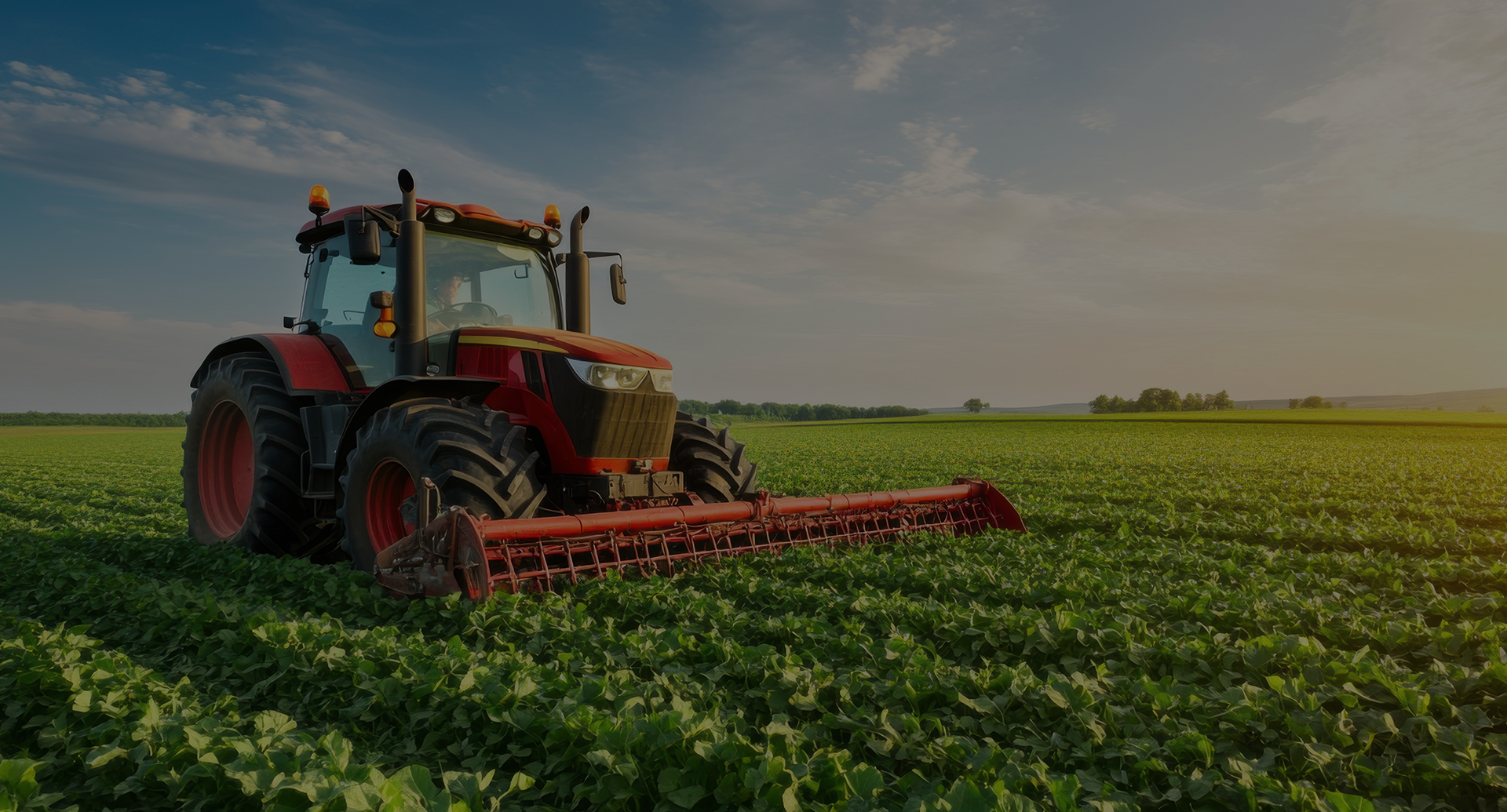
The many facets of the agricultural world
A comprehensive tour of the agricultural sector: discover the farming practices, livestock breeding and technological tools that shape today’s agriculture.
Essential machines of modern agriculture
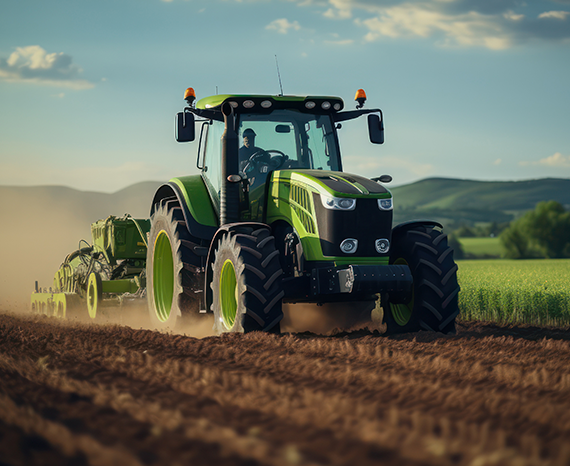

Tractor
A versatile machine for pulling agricultural implements.

Combine harvester
Harvests and separates grain.

Sprayer
Spreads products to protect crops.
The diversity of agricultural crops
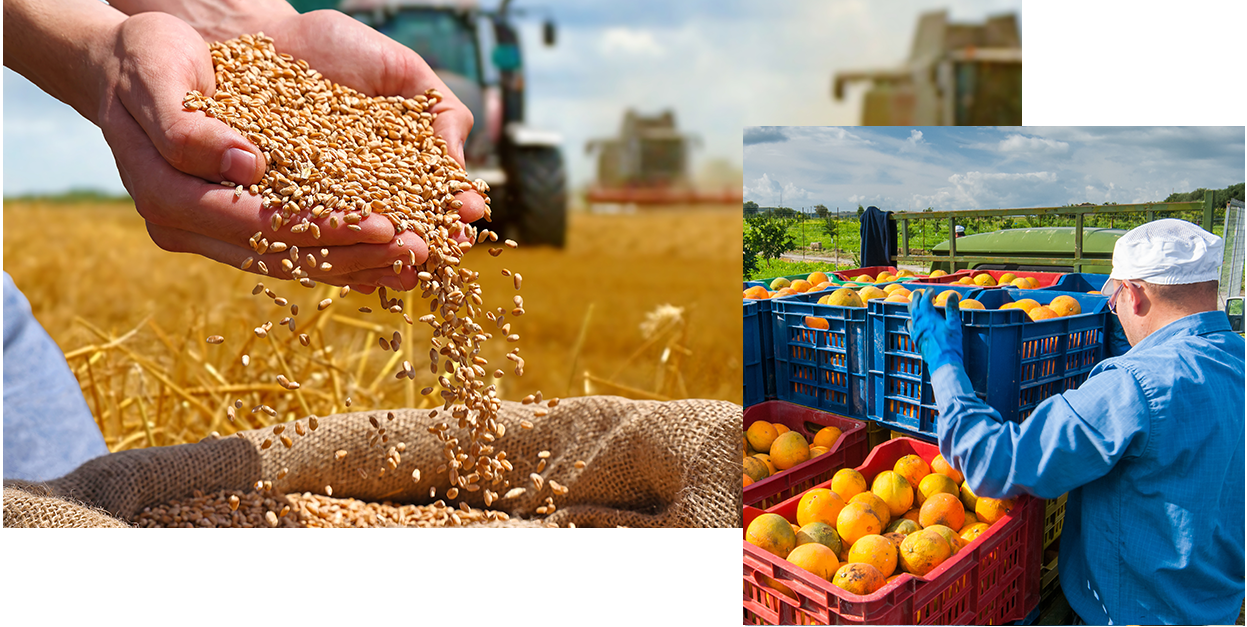
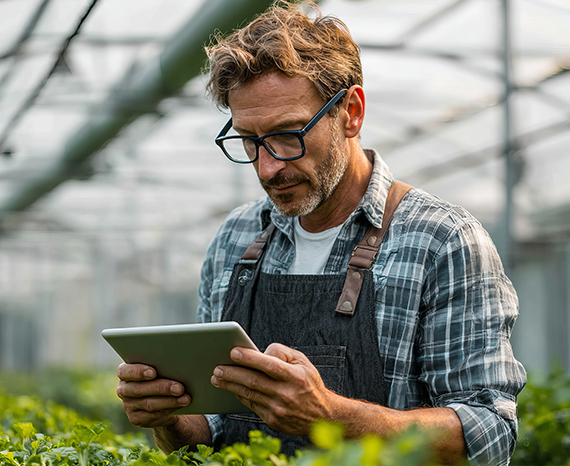


Farm organization and management
To ensure the success of a farm, rigorous organization is essential. This involves precise crop planning, careful management of financial and material resources, and regular monitoring of equipment. Effective staff coordination and compliance with environmental standards also contribute to optimizing productivity while ensuring the sustainability of the farm.
Adopting modern tools and appropriate methods helps improve decision-making and anticipate challenges related to the agricultural sector.
Farm life: a daily life influenced by nature
Every day on the farm is deeply connected to natural rhythms. Sunrise often marks the beginning of a busy day, with seasonal tasks: sowing, irrigating, harvesting, or caring for animals. Farmers live in harmony with the weather and biological cycles, which directly influence their activities.
This close connection with nature forges a way of life where patience, observation, and adaptation are essential to ensure the farm’s prosperity.

Cereal crops
Vegetable crops
Vegetable crops involve the production of fresh vegetables such as tomatoes, carrots, lettuce, and peppers.
Industrial crops
Industrial crops include plants grown for processing into non-food products, such as sugar beets for sugar, sunflowers for oil, or cotton for textiles.
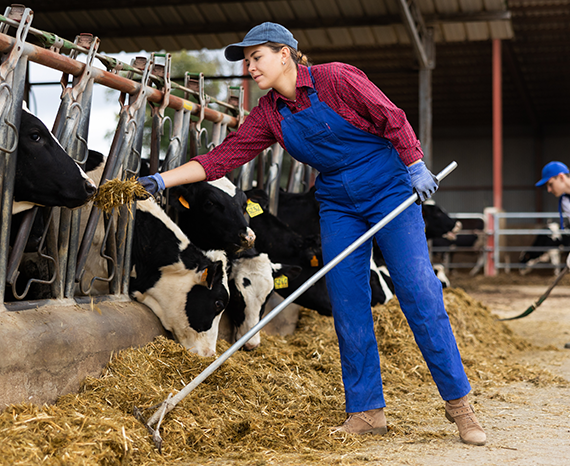
The main categories of livestock farming
Livestock farming plays an essential role in agriculture, providing a variety of products such as meat, milk, eggs, and wool. Each type of livestock farming meets specific needs: cattle are often used for meat and milk production, poultry farming primarily provides meat and eggs, while sheep are valued for their meat, wool, and sometimes milk.